 Alpha helix Alpha helix
a
helix is the most common secondary structure.
The polypeptide backbone of an
a
helix is wound around an imaginary axis, with the R groups of the amino acid residues protrude outward
from the helical backbone.
There is 3.6 a.a. per turn, and each turn extends 5.4 A in length which is maintained by the H-bond.
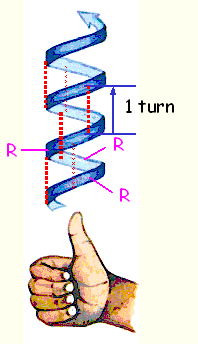
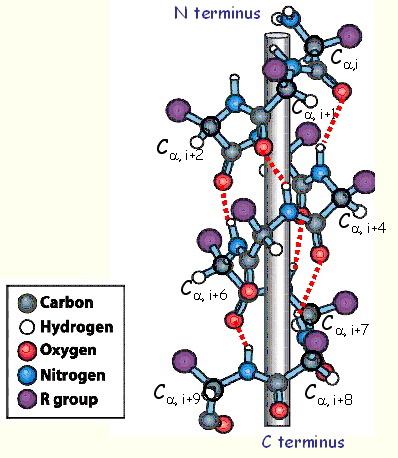
The
H-bond is formed between the -C
O
of residue (i) and the -N
H
of residue (i+3).
There are 2 H-bond per residue, and 3 or 4 H-bond per turn.
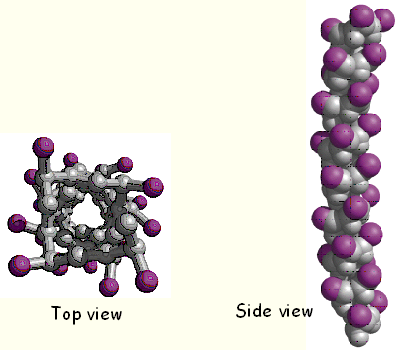
The ball-and-stick model of a right-handed
a
-helix, R group is represented by purple spheres.
 |